Galvanized Steel Barricades A Comprehensive Guide
Galvanized steel barricades are more than just barriers; they’re robust, versatile structures vital across numerous industries. From safeguarding construction sites to managing large-scale events, their strength and longevity make them indispensable. This guide delves into their design, construction, applications, and environmental impact, providing a complete picture of these crucial safety and security elements.
We’ll explore the properties of galvanized steel, comparing it to other materials and examining the galvanization process. We’ll also look at various barricade designs, manufacturing methods, and safety regulations. Finally, we’ll discuss maintenance, repair, and the environmental considerations surrounding their lifecycle.
Galvanized Steel Barricades

Source: made-in-china.com
Galvanized steel is a popular choice for barricade construction due to its robust nature and excellent resistance to the elements. This material offers a strong and durable solution for various applications, from temporary crowd control to more permanent security measures. Let’s delve into the specifics of why galvanized steel excels in this role.
Galvanized Steel Composition and Properties
Galvanized steel is essentially steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc. This zinc coating is what provides the superior corrosion resistance. The steel itself offers the strength and rigidity needed for a barricade, while the zinc safeguards it against rust and degradation. The thickness of the zinc coating, as well as the grade of steel used, determines the overall durability and lifespan of the barricade. Key properties include high tensile strength, good weldability, and relatively low cost compared to some alternatives.
The Galvanization Process and its Impact on Durability
The galvanization process typically involves dipping the steel into a molten zinc bath. This creates a metallurgical bond between the zinc and the steel, resulting in a durable and long-lasting coating. The thickness of this zinc layer directly impacts the barricade’s lifespan. A thicker coating provides more substantial protection against corrosion, extending the barricade’s service life significantly, often by decades compared to uncoated steel. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning to remove debris, can further enhance the lifespan of the galvanized steel barricade.
Corrosion Resistance Compared to Other Materials
Compared to other common barricade materials, galvanized steel demonstrates superior corrosion resistance. Aluminum, while also resistant to corrosion, is often less strong and more expensive. Plastics, while lightweight and relatively inexpensive, are generally less durable and more susceptible to damage from impact or extreme temperatures. The corrosion resistance of galvanized steel makes it ideal for outdoor applications where it’s exposed to harsh weather conditions, rain, snow, and salt spray, unlike plastic or even untreated steel which rusts quickly in these conditions.
Grades of Galvanized Steel and their Applications
Different grades of galvanized steel exist, each offering varying levels of strength and corrosion resistance. These grades are typically specified by standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials). Higher-grade galvanized steel, with thicker zinc coatings and stronger base steel, is often used in situations requiring exceptional durability, such as permanent security barricades or those exposed to extreme environmental conditions. Lower grades might suffice for temporary barricades in less demanding environments. The choice of grade depends heavily on the intended use and anticipated lifespan of the barricade.
Design and Construction of Galvanized Steel Barricades
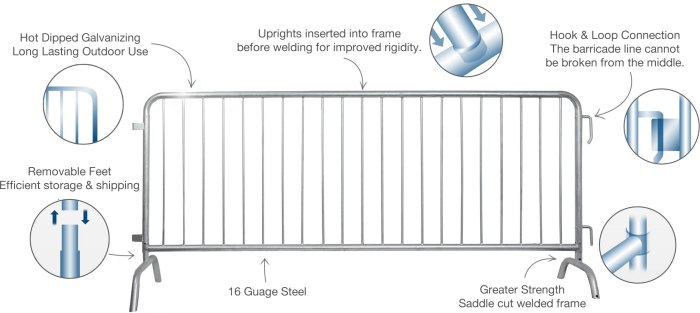
Source: startsafety.com
Galvanized steel barricades are crucial for a variety of applications, from construction sites to crowd control events. Their design and construction directly impact their durability, safety, and effectiveness. Understanding the different design elements and manufacturing processes is key to selecting and utilizing these barricades appropriately.
Barricade Designs and Structural Components
Several designs exist for galvanized steel barricades, each offering varying levels of strength, portability, and aesthetic appeal. These designs are optimized for different needs and environments. The choice of design depends heavily on the intended use and the anticipated level of impact or stress.
| Design Type | Weight (approx.) | Height (approx.) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Panel Barricade | 40-60 lbs | 36-42 inches | Interlocking panels, relatively lightweight, easy to transport and set up. Typically used for crowd control and temporary barriers. |
| Heavy-Duty K-Rail | 70-100 lbs | 42-48 inches | Stronger, more durable construction, is often used in construction zones or high-traffic areas. Can withstand significant impact. |
| Portable Barricade with Wheels | 50-80 lbs | 36-42 inches | Features wheels for easy mobility, suitable for quick setup and relocation. May be less stable than fixed barricades. |
| Modular Barricade System | Variable | Variable | Allows for customized configurations by connecting multiple sections. Highly versatile but may require more assembly time. |
Manufacturing Processes
The creation of galvanized steel barricades involves several key steps. First, steel sheets are cut and shaped to the desired dimensions using laser cutting or stamping machines. Then, the cut pieces undergo bending and forming processes to create the structural components of the barricade. Finally, the components are joined together using various methods (detailed in the next section) before undergoing the galvanization process, which protects the steel from corrosion.
Joining Methods, Galvanized steel barricades
Several joining methods are used in the construction of galvanized steel barricades, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Welding provides a strong and permanent connection, suitable for heavy-duty barricades. Bolting allows for easier disassembly and repair but may be slightly less robust than welding. Other methods, such as riveting, may also be employed depending on the specific design and intended application.
Safety Standards and Regulations
The design and construction of galvanized steel barricades must adhere to relevant safety standards and regulations to ensure the safety of workers and the public. These standards often specify requirements for material strength, structural integrity, and stability. Compliance with these regulations is essential to prevent accidents and ensure the barricades effectively perform their intended function. Examples of relevant standards may include OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulations in the United States or equivalent standards in other countries. Specific standards will vary depending on the intended use and location of the barricade.
Applications and Uses of Galvanized Steel Barricades

Source: vivablast.com
Galvanized steel barricades, thanks to their durability and versatility, find widespread use across numerous sectors. Their robust construction and resistance to corrosion make them a reliable choice for a variety of applications, from managing crowds at large events to providing crucial safety measures on construction sites. Understanding these applications and their specific needs helps determine the optimal barricade design and ensures effective deployment.
Construction Site Applications
Galvanized steel barricades are indispensable on construction sites, providing crucial safety barriers and delineating work zones. Their strength and resistance to damage are vital in environments where heavy machinery and materials are constantly in motion.
- Perimeter Security: Creating a secure boundary around the construction site, keeping unauthorized personnel out and ensuring worker safety.
- Traffic Control: Directing pedestrian and vehicular traffic safely through the site, preventing accidents, and maintaining order.
- Hazardous Area Delineation: Isolating areas containing hazardous materials or equipment, preventing accidental exposure or injury.
- Fall Protection: In certain situations, barricades can be used in conjunction with other safety measures to prevent falls from heights.
Event and Crowd Management Applications
From concerts and festivals to sporting events and political rallies, galvanized steel barricades are essential for managing large crowds safely and efficiently. Their ability to withstand significant impact is crucial in preventing crowd surges and maintaining order.
- Crowd Control: Guiding pedestrian flow, preventing overcrowding, and creating safe passageways.
- Stage and VIP Area Protection: Protecting performers and VIPs from the general public, ensuring their safety and security.
- Queue Management: Organizing lines and preventing bottlenecks, enhancing the overall event experience.
- Emergency Exits: Marking and protecting emergency exits, facilitating safe and rapid evacuation if necessary.
Security Applications
In security contexts, galvanized steel barricades offer a robust and visible deterrent to unauthorized access. Their strength and durability make them suitable for protecting sensitive areas or controlling access points.
- Perimeter Security: Creating a physical barrier around buildings or facilities, deterring intruders, and enhancing security.
- Access Control: Restricting access to specific areas, such as loading docks or restricted zones.
- Temporary Roadblocks: Creating temporary roadblocks during emergencies or security incidents.
- Protecting Critical Infrastructure: Shielding essential infrastructure, such as power stations or communication towers, from potential threats.
Case Study: A Large Music Festival
A major music festival utilized hundreds of galvanized steel barricades to manage crowd flow and create safe zones around stages and VIP areas. The barricades’ robust construction withstood the pressure of large crowds, preventing accidents and ensuring a safe and enjoyable event for attendees. The visible presence of the barricades also provided a sense of security and helped guide attendees effectively.
Advantages and Disadvantages Compared to Alternatives
Compared to alternative materials like plastic or wooden barricades, galvanized steel offers superior strength and durability, particularly in demanding environments. However, galvanized steel barricades are typically heavier and more expensive. Plastic barricades are lighter and cheaper but less durable and may not provide the same level of security. Wooden barricades offer a compromise but are susceptible to rot and damage. The choice of material depends heavily on the specific application and the balance between cost, durability, and security needs.
Maintenance and Longevity of Galvanized Steel Barricades

Source: made-in-china.com
Proper maintenance significantly extends the lifespan of galvanized steel barricades, ensuring their continued effectiveness and safety. Regular inspections and cleaning prevent corrosion and damage, ultimately saving money on costly repairs or replacements in the long run. This section details a practical maintenance schedule and repair procedures.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A consistent maintenance schedule is crucial. This involves both regular cleaning and thorough inspections. Neglecting either can lead to premature deterioration and compromise the barricade’s structural integrity. For high-traffic areas or harsh environments, more frequent maintenance is recommended.
A sample schedule might look like this:
- Daily: Quick visual inspection for obvious damage, such as dents, loose bolts, or significant rust.
- Weekly: More thorough inspection, checking welds, hinges, and any moving parts. Remove any loose debris or dirt.
- Monthly: Complete cleaning using a pressure washer (low pressure to avoid damage) and a mild detergent. Pay close attention to areas prone to corrosion, such as joints and welds.
- Annually: Comprehensive inspection by a qualified professional. This includes checking for structural weaknesses, and significant corrosion, and addressing any necessary repairs.
Common Types of Damage and Repair Methods
Several factors contribute to damage. These include impacts from vehicles, vandalism, environmental exposure (e.g., extreme temperatures, salt spray), and general wear and tear. Knowing the common types of damage allows for quicker identification and appropriate repair strategies.
Here are some examples:
- Dents and Scratches: Minor dents and scratches can often be addressed with careful straightening and repainting with a zinc-rich primer and a topcoat of weather-resistant paint.
- Rust: Rust is a serious issue and requires immediate attention. Remove all loose rust using a wire brush, treat the affected area with a rust converter, and apply a zinc-rich primer followed by durable paint.
- Broken or Loose Bolts: Replace any broken or loose bolts with appropriately sized and galvanized replacements. Ensure they are tightened securely.
- Cracked or Damaged Welds: This requires professional attention. A welder will need to repair or replace the damaged weld. This should only be done by a qualified welder to ensure structural integrity.
Factors Affecting Longevity
The lifespan of galvanized steel barricades is influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors allows for proactive measures to enhance their longevity.
Key factors include:
- Environmental Conditions: Coastal areas with high salinity and regions with frequent freeze-thaw cycles experience accelerated corrosion. Barricades in these environments may require more frequent maintenance.
- Usage Patterns: High-impact areas or those subjected to frequent movement or collisions will degrade faster than those in less demanding settings. Consider using reinforced barricades in high-impact areas.
- Quality of Galvanization: The thickness and quality of the galvanization coating significantly affect corrosion resistance. Thicker coatings provide better protection.
Repairing Minor Damage: A Step-by-Step Guide
For minor damage, such as small dents or scratches, repairs can often be performed in-house.
Follow these steps:
- Assessment: Carefully assess the extent of the damage. If the damage is significant or compromises structural integrity, seek professional help.
- Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the damaged area with a wire brush to remove any loose rust, dirt, or debris.
- Rust Treatment (if necessary): If rust is present, apply a rust converter to neutralize the rust and prepare the surface for priming.
- Priming: Apply a zinc-rich primer to protect the bare metal from further corrosion. Allow the primer to dry completely.
- Painting: Apply a durable, weather-resistant paint in several thin coats, allowing each coat to dry completely before applying the next.
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific primer and paint used.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability

Source: soncostore.net
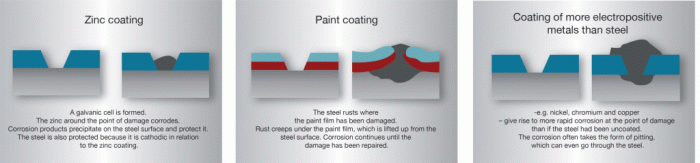
Galvanized steel barricades, while robust and long-lasting, have an environmental footprint that needs careful consideration. Their lifecycle, from raw material extraction to eventual disposal, impacts the environment in various ways. Understanding this impact and implementing sustainable practices are crucial for minimizing their negative effects.
The manufacturing process of galvanized steel barricades involves several stages with associated environmental impacts. Iron ore mining and processing release pollutants into the air and water. Steel production is energy-intensive, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. The galvanization process, which involves coating the steel with zinc to protect it from corrosion, also uses energy and produces zinc-containing waste. Disposal of these barricades, if not properly managed, can lead to landfilling and potential leaching of zinc into the soil and water.
Recyclability of Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel boasts excellent recyclability compared to many other barricade materials such as plastic or wood. The zinc coating doesn’t significantly hinder the recycling process. Steel can be melted down and reused numerous times without losing its structural integrity. This inherent recyclability contributes to a smaller environmental footprint compared to materials with limited or no recycling options. For example, plastic barricades often end up in landfills, contributing to plastic pollution, while wood barricades can decompose, releasing greenhouse gasses. The high recyclability rate of steel reduces the demand for virgin materials, conserving natural resources and decreasing energy consumption.
Sustainable Practices in Production and Lifecycle Management
Several sustainable practices can significantly reduce the environmental impact of galvanized steel barricades. These include using recycled steel in the manufacturing process, optimizing energy efficiency in steel production and galvanization, and implementing robust end-of-life management programs that prioritize recycling. Companies are increasingly adopting cleaner production technologies that minimize waste and pollution. For instance, some manufacturers utilize closed-loop water systems to reduce water consumption and prevent the discharge of pollutants. Furthermore, designing barricades for easy disassembly and component separation simplifies recycling and maximizes material recovery. Investing in efficient transportation routes to reduce carbon emissions during delivery also contributes to overall sustainability.
Initiatives and Technologies for Minimizing Environmental Footprint
Various initiatives and technologies are being developed to further minimize the environmental impact of galvanized steel barricades. Research into more energy-efficient steel production methods, such as the use of hydrogen in steelmaking, is ongoing. Improved zinc coating techniques can reduce zinc waste and improve the durability of the barricades, extending their lifespan. Furthermore, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are being used to evaluate the environmental performance of different barricade materials and designs, informing more sustainable choices. Government regulations and industry standards are also playing a role in promoting the use of recycled steel and responsible disposal practices. Incentives for recycling and extended producer responsibility schemes encourage manufacturers to take responsibility for the end-of-life management of their products.
End of Discussion: Galvanized Steel Barricades
Source: nordicgalvanizers.com
Galvanized steel barricades offer a robust and reliable solution for a wide range of applications, combining strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding their design, construction, and maintenance ensures their effective and safe use, while also considering their environmental impact promotes sustainable practices. By carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages, you can make informed decisions about utilizing these essential safety barriers.





