Commercial Gate Repair Solutions & Maintenance
Commercial gate repair is more than just fixing a broken gate; it’s about ensuring the safety and security of your business. From the sturdy swing gates of a warehouse to the sleek sliding gates of a high-security facility, the smooth operation of your commercial gates is crucial. This guide dives into the common issues, repair methods, and preventative maintenance strategies to keep your gates functioning flawlessly and your business running smoothly.
We’ll explore different gate types, materials, and common problems, offering practical solutions and cost considerations. Learn how to choose a reliable repair service and understand the importance of safety precautions during any repair work. Whether you’re dealing with a simple hinge problem or a complex automated gate malfunction, we’ve got you covered.
Types of Commercial Gates

Source: gaterepairexperts.com
Choosing the right commercial gate is crucial for security, efficiency, and aesthetics. Different gate types offer varying levels of security, ease of use, and suitability for different environments. Understanding the materials and applications of each type will help you make an informed decision.
Commercial Gate Types and Their Components
Commercial gates are broadly categorized based on their opening mechanism. Each type has specific components that contribute to its functionality and durability. Common components include the gate leaves (the moving parts), the frame, hinges, rollers, tracks, operators (for automated gates), and locking mechanisms.
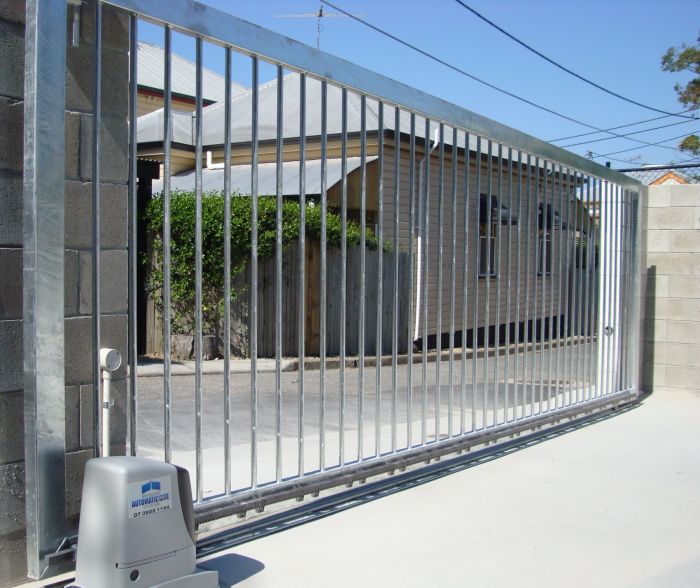
Sliding Gates
Sliding gates move horizontally along a track, opening by sliding to the side. They are popular for their space-saving design, as they don’t require swing space. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and sometimes wood for smaller applications. Steel offers high strength and durability, aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, while wood provides a more aesthetically pleasing option but requires more maintenance. Sliding gates are frequently used in industrial settings, warehouses, and parking garages where space is limited.
| Gate Type | Material | Common Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sliding Gate | Steel, Aluminum, Wood | Industrial facilities, warehouses, parking garages | Space-saving, simple operation, high security (with proper locking mechanisms) |
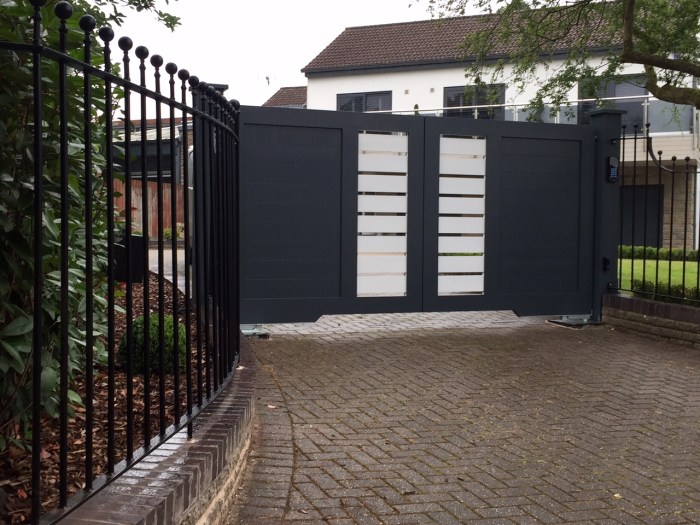
Swing Gates
Swing gates open and close by swinging inward or outward on hinges. They are a classic and versatile option suitable for various applications. Materials commonly used are steel, aluminum, and wrought iron. Steel provides robustness, aluminum offers lightweight durability, and wrought iron adds an elegant, decorative touch. Swing gates are commonly found at residential complexes, commercial entrances, and industrial sites where space allows for their arc of movement. Imagine a large, ornate wrought iron gate at a stately office building, or simpler steel gates at a warehouse loading dock.
| Gate Type | Material | Common Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swing Gate | Steel, Aluminum, Wrought Iron | Commercial entrances, residential complexes, industrial sites | Versatile, aesthetically pleasing (especially wrought iron), relatively simple design |
Rolling Gates
Rolling gates consist of horizontal slats that roll up and down vertically, similar to a garage door. They are often made of steel or aluminum, with steel offering superior strength and aluminum providing corrosion resistance and lighter weight. Rolling gates are frequently used in storefront security, warehouse openings, and industrial settings where compact storage and quick opening/closing are important. Visualize a small retail store using a rolling gate to secure its storefront overnight, or a large warehouse using a motorized rolling gate for efficient loading and unloading.
| Gate Type | Material | Common Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rolling Gate | Steel, Aluminum | Storefronts, warehouses, industrial settings | Space-saving when open, quick operation, good security |
Materials and Their Properties
The choice of material significantly impacts the gate’s lifespan, maintenance requirements, and overall cost. Steel is strong and durable but can rust if not properly treated. Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and relatively easy to maintain. Wood offers an aesthetic appeal but requires regular maintenance to prevent rot and insect damage. The selection should consider the specific environmental conditions and security needs.
Common Commercial Gate Repair Issues

Source: gaterepairexperts.com
Keeping your commercial gate in top working order is crucial for security, smooth operations, and overall business efficiency. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs and even security breaches. Understanding common problems and implementing preventative measures is key to avoiding these issues. In this section Artikels five frequent problems encountered in commercial gate repair, their causes, and practical preventative strategies.
Gate Operator Malfunctions
Gate operator malfunctions are a leading cause of commercial gate repair calls. These issues range from simple sensor problems to more complex motor failures. Causes include wear and tear from constant use, exposure to harsh weather conditions (like extreme heat or cold), power surges, and even attempts at forced entry. Preventative maintenance significantly reduces the likelihood of these problems.
- Regular lubrication of moving parts helps reduce friction and wear.
- Annual inspection by a qualified technician to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
- Installation of surge protectors to safeguard the operator from power fluctuations.
- Regular cleaning of sensors and photo eyes to ensure proper functioning.
Damaged Gate Components
Commercial gates consist of many moving parts, all susceptible to damage. This can include bent or broken gate arms, damaged rollers, broken springs, or malfunctioning hinges. The causes are varied, encompassing accidental impacts from vehicles, vandalism, and general wear and tear from frequent use. A proactive maintenance approach can minimize these issues.
- Regular visual inspections to identify any signs of damage or wear.
- Prompt repair or replacement of damaged components to prevent further damage.
- Reinforcement of vulnerable areas, such as gate posts, to withstand impacts.
- Consider using more durable materials for gate construction in high-traffic or vulnerable areas.
Electrical Problems
Electrical issues in commercial gates, such as faulty wiring, blown fuses, or short circuits, are common. These can stem from improper installation, damage from weather, or even rodent activity. Regular checks and preventative maintenance are vital to ensure the gate’s electrical system remains reliable.
- Regular inspection of all wiring and connections for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Ensuring proper grounding to prevent electrical shocks and damage.
- Use of weatherproof electrical components to protect against moisture damage.
- Regular testing of safety features, such as emergency stop buttons and sensors.
Security System Failures
Commercial gates often incorporate security systems, including access control systems, alarm systems, and video surveillance. Failures in these systems can compromise security. Causes range from software glitches and hardware malfunctions to vandalism and attempted breaches. A robust preventative maintenance plan is crucial.
- Regular software updates to address vulnerabilities and improve performance.
- Regular testing of all security components to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Routine checks for signs of tampering or vandalism.
- Implementing a strong access control policy to limit unauthorized access.
Foundation Issues
The gate’s foundation is critical for its stability and longevity. Problems such as settling, cracking, or erosion can lead to misalignment and damage to the gate and its components. These issues are often caused by poor initial installation, ground movement, or environmental factors. Preventing foundation problems requires careful planning and ongoing monitoring.
- Regular inspection of the gate’s foundation for any signs of settling, cracking, or erosion.
- Proper drainage around the gate to prevent water accumulation and erosion.
- Professional assessment and repair of any foundation problems as soon as they are identified.
- Ensuring the gate’s foundation is properly designed and installed to withstand the expected loads.
Repair Methods and Procedures

Source: gaterepairlaverne.com
Commercial gate repair requires a systematic approach, combining diagnostic skills with practical knowledge of gate mechanics. Understanding the various components and their functions is crucial for effective repairs. This section Artikels procedures for common repair tasks.
Damaged Gate Operator Repair
Repairing a damaged gate operator often involves troubleshooting electrical components and mechanical linkages. First, visually inspect the operator for any obvious damage like loose wiring, broken parts, or physical obstructions. Next, check the power supply and ensure the circuit breaker hasn’t tripped. If the power is good, test the control board for any error codes displayed on a digital readout or through indicator lights. If a code is present, consult the operator’s manual for troubleshooting guidance. Often, replacing a faulty control board or motor is necessary. If the problem is mechanical, such as a damaged gear or limit switch, these components may need to be replaced or adjusted. Always disconnect the power before working on any electrical components. Following the manufacturer’s instructions for reassembly and testing is essential.
Hinge Repair
Commercial gate hinges are subjected to significant stress. Regular inspection for wear and tear is vital. Repair usually involves tightening loose screws or replacing damaged hinges. If a hinge is bent or broken, it must be replaced. Before replacing a hinge, carefully note the hinge placement and orientation to ensure correct reinstallation. Use appropriately sized screws and ensure they are securely fastened. Proper alignment is key to smooth gate operation and prevents further damage.
Roller and Track Repair
Rollers and tracks are critical for smooth gate movement. Damaged rollers can cause binding, noise, and uneven operation. Repair involves inspecting the rollers for wear, cracks, or damage. Replacing worn rollers is often necessary. Clean and lubricate the tracks to reduce friction. If the tracks are bent or damaged, they may need to be straightened or replaced. Consider the material of the tracks (e.g., steel, aluminum) when selecting replacement parts to ensure compatibility and durability. Ensure the rollers are properly aligned within the tracks to avoid premature wear.
Troubleshooting Flowchart for a Malfunctioning Commercial Gate
A flowchart can help systematically diagnose gate malfunctions. This example focuses on a gate that won’t open or close.
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would start with a box labeled “Gate Malfunction?”. This would branch to “Check Power Supply” (yes/no). If yes, it would branch to “Check Control Board for Error Codes” (yes/no). If yes, it would branch to “Consult Manual for Code Troubleshooting”. If no to the power supply check, it would branch to “Check Circuit Breaker”. If no to the control board error codes, it would branch to “Check Mechanical Components (hinges, rollers, tracks)”. Each of these branches would have further branches for specific troubleshooting steps and potential solutions. The flowchart would ultimately lead to a box indicating the likely cause of the malfunction and the necessary repair.]
Safety Precautions During Gate Repair

Source: metrogaragedoor.net
Commercial gate repair presents various hazards. Prioritizing safety is crucial for preventing injuries and ensuring efficient repairs. This section Identifies essential safety measures and strategies for mitigating potential risks. Always remember that safety should be your top priority, even above the speed of completion.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with commercial gates. Failing to use the correct PPE can lead to serious injuries. The specific PPE required will vary depending on the nature of the repair but generally includes items like safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from flying debris, work gloves to protect your hands from cuts and abrasions, sturdy work boots to protect your feet from falling objects or crushing, and hearing protection if working with noisy equipment. For tasks involving heights or working on elevated platforms, a safety harness and fall protection system are necessary. When working with potentially hazardous materials like chemicals or lubricants, appropriate respiratory protection is also crucial.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
The following table details common hazards encountered during commercial gate repair and effective mitigation strategies:
| Hazard | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Falling objects (gate parts, tools) | Secure loose parts before starting work. Use proper lifting techniques. Ensure a clear work area free of obstructions. Wear a hard hat. |
| Crushing injuries (from moving gate parts) | Disconnect power sources before working on electric gates. Use appropriate blocking or shoring to prevent unintended movement. Never work under a suspended gate section without proper support. |
| Cuts and lacerations (from sharp edges, tools) | Wear cut-resistant gloves. Use caution when handling sharp tools and materials. Inspect gate components for sharp edges before beginning work and take steps to protect yourself from them. |
| Electrocution (from electrical components) | Always disconnect power before working on electric gates. Use insulated tools. Verify that the power is off using a voltage tester. |
| Chemical burns (from lubricants, cleaning agents) | Wear appropriate protective gloves and eye protection. Use chemicals in well-ventilated areas. Follow the manufacturer’s safety instructions for all chemicals used. |
| Struck-by hazards (from swinging gates) | Use appropriate blocking or bracing to prevent accidental movement of the gate. Warn others in the area of the potential hazard. |
| Falls from heights (during elevated work) | Use appropriate fall protection equipment, such as a safety harness and lanyard. Ensure a stable work platform. |
| Noise-induced hearing loss (from power tools) | Wear hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, when operating noisy equipment. |
Cost Considerations for Commercial Gate Repair

Source: allprodoor.com
Repairing or replacing a commercial gate can be a significant expense. Understanding the cost factors involved is crucial for budgeting and making informed decisions. This section breaks down the typical costs associated with various repair scenarios and compares repair to replacement costs.
Typical Costs of Commercial Gate Repair
The cost of commercial gate repair varies greatly depending on the type of gate, the extent of the damage, the required materials, and the labor involved. The following table provides a general estimate of labor and material costs for common repair scenarios. Keep in mind that these are averages and actual costs may vary based on location and specific circumstances.
| Repair Type | Labor Cost (USD) | Material Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Broken Spring Repair (Single) | 150-300 | 50-150 |
| Broken Spring Repair (Double) | 300-600 | 100-300 |
| Operator Repair (Minor Electrical Issue) | 200-400 | 50-150 |
| Operator Replacement | 500-1000 | 500-1500 |
| Roller Replacement (Single) | 100-200 | 25-75 |
| Gate Panel Repair (Minor Damage) | 150-300 | 50-200 |
| Gate Panel Replacement | 300-600 | 200-800 |
Repair Versus Replacement Costs
Repairing a damaged gate is generally cheaper than replacing it entirely. However, if the damage is extensive or the gate is old and outdated, replacement might be a more cost-effective long-term solution. For example, repairing multiple broken springs on an aging gate might cost close to the price of a new gate, making replacement the more sensible option. Consider the overall condition of the gate, its remaining lifespan, and the cost of future repairs when making this decision.
Factors Influencing Commercial Gate Repair Costs
Several factors influence the final cost of commercial gate repair. These include:
* Type of Gate: Larger, more complex gates (e.g., sliding gates, cantilever gates) typically cost more to repair than simpler gates (e.g., swing gates).
* Extent of Damage: Minor repairs are naturally less expensive than major repairs requiring extensive parts replacement or structural work.
* Materials Used: The cost of materials varies depending on the quality and type of materials used (e.g., steel, aluminum, wood). Higher-quality materials usually mean higher repair costs but also increased durability.
* Labor Rates: Labor rates vary depending on the location, the experience of the repair technician, and the urgency of the repair. Emergency repairs often come with higher labor charges.
* Accessibility: Difficult-to-access gates may require additional labor costs for equipment or specialized techniques.
Choosing a Commercial Gate Repair Service

Source: sanantoniogaragedoorandgate.com
Choosing the right commercial gate repair service is crucial for ensuring the safety and security of your property. A poorly chosen service can lead to inadequate repairs, further damage, and even safety hazards. Taking the time to research and select a reputable company will save you time, money, and potential headaches in the long run.
Selecting a reputable commercial gate repair company requires careful consideration of several key factors. These factors directly impact the quality of service received, the longevity of the repairs, and the overall cost-effectiveness of the project.
Criteria for Selecting a Reputable Commercial Gate Repair Company
Several factors should guide your decision-making process when selecting a commercial gate repair service. These factors range from licensing and insurance to customer reviews and warranties. A thorough assessment will ensure you choose a provider capable of meeting your specific needs.
- Licensing and Insurance: Verify that the company holds all necessary licenses and carries adequate liability insurance. This protects you from potential financial liabilities in case of accidents or damages during the repair process. A reputable company will readily provide proof of insurance and licensing upon request.
- Experience and Expertise: Look for a company with extensive experience in repairing commercial gates of various types and sizes. Inquire about their experience with the specific type of gate you have. A company with a proven track record is more likely to deliver quality workmanship.
- Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Check online reviews and testimonials from previous clients. These provide valuable insights into the company’s reliability, responsiveness, and quality of their work. Look for consistent positive feedback across multiple platforms.
- Warranty and Guarantees: A reputable company will offer a warranty or guarantee on their repairs. This shows confidence in their work and provides you with recourse if problems arise after the repair is completed. Inquire about the duration and specifics of their warranty.
- Pricing and Payment Terms: Obtain detailed quotes from multiple companies before making a decision. Compare pricing structures and payment terms to ensure you’re getting a fair price for the services rendered. Be wary of companies with unusually low or high prices.
Finding Qualified and Insured Technicians
Ensuring your chosen technicians are qualified and insured is paramount for a successful and safe repair. This involves more than simply asking; it necessitates verification of credentials and insurance coverage.
- Verification of Credentials: Request copies of certifications, licenses, and training records for the technicians who will be working on your gate. This allows you to confirm their expertise and experience in gate repair.
- Insurance Verification: Ask for proof of liability insurance and workers’ compensation insurance. This safeguards you against potential financial liabilities in case of accidents or injuries during the repair process.
- Background Checks: For added security, consider requesting background checks on the technicians. This is especially important for companies that require access to your property outside of regular business hours.
- References: Request references from previous clients. Contacting these clients allows you to gather firsthand accounts of the company’s professionalism, reliability, and the quality of their work.
In-House versus Outsourced Repair Services
The decision of whether to utilize in-house or outsourced repair services depends on various factors, including budget, available resources, and the frequency of gate repairs. Each option presents distinct advantages and disadvantages.
- In-House Repair Services: Advantages include greater control over the repair process, potential cost savings in the long run (if repairs are frequent), and better integration with existing maintenance schedules. Disadvantages include the need for specialized training and equipment, higher initial investment costs, and potential downtime if your in-house team is unavailable.
- Outsourced Repair Services: Advantages include access to specialized expertise, readily available resources, and reduced administrative overhead. Disadvantages include potential higher costs per repair, less control over the repair process, and potential scheduling conflicts.
Gate Automation and Repair

Source: gaterepairexperts.com
Automating your commercial gates offers significant advantages, including increased security, convenience, and efficiency. However, understanding the different automation systems and how to troubleshoot common issues is crucial for maintaining smooth operations and minimizing downtime. This section will cover the most prevalent automation types and provide practical guidance on addressing typical problems.
Commercial gates can be automated using various systems, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice often depends on factors like gate size, weight, security needs, and budget.
Types of Gate Automation Systems
Electric operators are the most common type of gate automation. They use electric motors to drive the gate’s opening and closing mechanisms. These motors can be powered by either AC or DC electricity and typically incorporate a control board to manage various functions, such as speed control, safety sensors, and emergency stops. Smaller, lighter gates might use swing arm operators, while larger, heavier gates often require sliding gate operators with more robust gearing. Hydraulic systems, on the other hand, utilize hydraulic cylinders and pumps to generate the force needed to move the gate. They are generally preferred for very heavy gates or those operating in extreme weather conditions due to their superior power and durability. However, they are typically more expensive to install and maintain than electric systems.
Troubleshooting Automated Gate Problems
Malfunctioning sensors are a frequent cause of automated gate issues. These sensors, usually photoelectric or radar-based, detect obstructions in the gate’s path and prevent it from closing on anything. If a sensor is malfunctioning, the gate may not open or close at all, or it may stop abruptly mid-cycle. Troubleshooting involves checking for obstructions, loose wiring, and sensor alignment. Cleaning the sensor lenses is often sufficient to restore functionality. Power failures can also cause problems, resulting in a completely inoperable gate. Check the power supply, fuses, and circuit breakers to ensure the gate receives power. If the problem persists, contact a qualified electrician.
Components of a Typical Automated Gate System, Commercial gate repair
A simple diagram of a typical automated gate system would show the following components: the gate itself (whether swing or sliding), an electric motor (or hydraulic cylinder), a control box containing the circuitry and safety features, sensors (photoelectric or radar), a power supply, and limit switches (to signal when the gate is fully open or closed). The motor is connected to the gate via a chain or gear mechanism, and the sensors are positioned to detect obstacles. The control box receives signals from the sensors and other components and manages the motor’s operation, ensuring safe and efficient gate movement. The power supply provides electricity to the motor and control box, while limit switches prevent the gate from moving beyond its designated open and closed positions. Wiring connects all components, allowing for communication and control. The diagram could show these elements linked visually, clearly indicating the flow of power and signals.
Final Review: Commercial Gate Repair

Source: placergaragedoorgaterepair.com
Keeping your commercial gates in top condition is a proactive approach to security, efficiency, and cost savings. By understanding the common problems, preventative maintenance techniques, and proper repair procedures, you can minimize downtime and ensure the longevity of your gates. Remember, choosing a qualified and insured repair service is key to a successful and safe repair. Investing in regular maintenance is far more cost-effective than emergency repairs, safeguarding your business and its operations.